-
PLD’s Whole School Literacy Plan
The document outlines how to implement PLD's literacy, Movement and Motor and Oral Language resources during the Early Years, Foundation, Year 1 & 2 and across Years 3 to 6. Each page provides suggested time frames and implementation recommendations.The purpose of this document is to provide an implementation outline to assist schools in scheduling the PLD programs within a broad school-based strategy. When
-
Private: Maximising literacy development within the Junior Primary
At PLD we advocate for a strong junior primary process, in which the connections between classrooms and year levels is well organised. Most students require
-
The Pathway of Pre-Literacy into Early Literacy
Schools will have literacy results maximized over the long-term when they systematically plan how students progress from pre-literacy (or emergent literacy skills) into their early
-
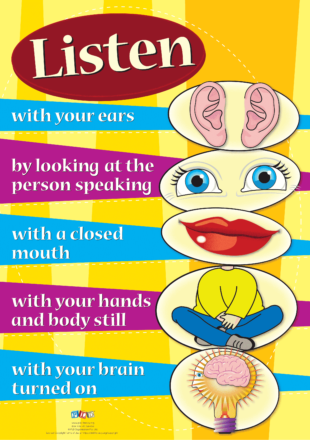
Listen A3 poster
To Create A Good Speaking And Listening EnvironmentBrainstorm with students what makes a good listener and speaker. Have a reward system that promotes good listening and speaking behaviours in the classroom. Give
Teach a Child to Read in 3 steps
Code: CCread
Year Level: Year 1 & 2
$82.50 (inc. $7.50 GST)
Targeting alphabet sounds, phonemic blending and CVC decoding
Single word decoding involves two primary base skills:
- Visual Skills: The recognition of the alphabet symbol and the conversion of this symbol into a sound (ie: Not letter name).
- Auditory Skills: The phonemic awareness skill of blending three sounds (or phonemes) together to form a word.
The following example illustrates the process of early decoding. To read the word ‘sit’ a student must:
- Visually recognise the symbol ‘s’ and convert the symbol to the sound /s/.
- Visually recognise the symbol ‘i’, and convert the symbol into the sound /i/.
- Visually recognise the symbol ‘t’, and convert the symbol into the sound /t/.
- Finally, the ‘s’, ‘i’ and ‘t’ sounds are held in the working memory, then need to be blended together to form the word.
Over time children become more efficient at a visual and an auditory level. For example, rather than decoding the word ‘sit’ in three parts the word may be decoded in two parts (e.g. s-it). After much decoding practice students develop automatic word recognition and will read the word in full without sounding.
The other programs within the range include:
This publication is mentioned within the Year 1 & 2 Teaching Sequence Manual on page 19.
Teach a Child to Read in 3 steps - eBook
Code: CCread
Year Level: Year 1 & 2
$65.00 (inc. $5.91 GST)
Targeting alphabet sounds, phonemic blending and CVC decoding
Single word decoding involves two primary base skills:
- Visual Skills: The recognition of the alphabet symbol and the conversion of this symbol into a sound (ie: Not letter name).
- Auditory Skills: The phonemic awareness skill of blending three sounds (or phonemes) together to form a word.
The following example illustrates the process of early decoding. To read the word ‘sit’ a student must:
- Visually recognise the symbol ‘s’ and convert the symbol to the sound /s/.
- Visually recognise the symbol ‘i’, and convert the symbol into the sound /i/.
- Visually recognise the symbol ‘t’, and convert the symbol into the sound /t/.
- Finally, the ‘s’, ‘i’ and ‘t’ sounds are held in the working memory, then need to be blended together to form the word.
Over time children become more efficient at a visual and an auditory level. For example, rather than decoding the word ‘sit’ in three parts the word may be decoded in two parts (e.g. s-it). After much decoding practice students develop automatic word recognition and will read the word in full without sounding.
The other programs within the range include:
This publication is mentioned within the Year 1 & 2 Teaching Sequence Manual on page 19.
Teach a Child to Read in 3 steps – School Licence
This product is currently not available as a School Licence.
A School Licence is a multi-user subscription to a PLD resource, such as a book or program, in a digital and printable format that is available on all devices.
A School Licence is valid for 12 months from the date of purchase and can be used by an unlimited number of teachers within a school.
To read more about school licencing and to view the full range of licenced publications select PLD School Licences
Below you will find a range of FAQ'S related to school licences:
- What is a PLD School Licence?
- What are the benefits of a School Licence?
- What PLD resources are available to buy under a School Licence?
- Who should purchase the School Licence?
- How do I purchase a School Licence?
- How do I add a teacher to a School Licence?
- How do I remove a teacher from a School Licence?
- I don’t know whether to buy a School Licence or an EBook.
- Can I share my School Licence with teachers from other schools?
- Can I store a school licened resource on my school’s server?
- Can I print out copies of the digital versions?
Books: PLD’s books may only be used by the Authorised Purchaser, and the Authorised Purchaser’s students, and only in conjunction with classes taken by the Authorised Purchaser. PLD’s books may be photocopied up to 10% per year for use only by the Authorised Purchaser. The Authorised Purchaser is defined as the original purchaser of the PLD materials.
eBooks: PLD’s eBooks may only be used by the Authorised Purchaser, and the Authorised Purchaser’s students, and only in conjunction with classes taken by the Authorised Purchaser. The Authorised Purchaser is defined as the original purchaser of the PLD eBook. Under the ‘Statutory Educational Licence’ the authorised purchaser can:
- View the eBook as a whole or in part
- Copy the eBook to their personal drive or locally on their device
- Display the eBook on your Interactive Whiteboard, projector or smart TV, for the purpose of teaching the students in their own classroom
- Photocopy or print up to 10% of the eBook per year, for use with the students in their classroom(s).
For copyright purposes, every page of the PLD eBooks will be stamped with the name & email address provided by the purchaser at the time of order. PLD ebooks belong solely to the purchaser and may not be shared with colleagues, parents or anyone else. PLD eBooks must not be uploaded to school servers, intranets or online platforms. Schools wishing to licence PLD eBooks can contact us HERE.
School Licences: A School Licence is a multi-user subscription to a PLD resource, such as a book or program, in a digital and printable format that is accessible via the ‘My Subscription’ section of the PLD website. A School Licence is valid for 12 months from the date of purchase and can be used by an unlimited number of teachers within a school. When bought under a School Licence:
- Resources are accessible in digital, flipbook format, which teachers can access from anywhere, at any time, on any device via the PLD website.
- The resources can be used by any amount of teachers in that school.
- Multiple teachers can access the resources simultaneously.
- The resource is available to print, subject to the standard 10% per year limitation as per Australian Copyright law.
- Updated versions of resources will be automatically accessible to users with a current licence for free, ensuring all users have access to the latest versions of resources.
- Resources are stored centrally and accessed via a secure login account on the PLD website. Thus, all currently subscription resources are accessible in the one convenient place, making resources extremely easy to find. Moreso, the school licence offering eradicates the frustration of lost or misplaced resources and programs which happens often with hardback books.
Additional information can be accessed via the following links:
Books: https://support.pld-literacy.org/en-au/article/plds-printed-electronic-materials-how-can-they-be-used-can-i-share-them-with-a-friendcolleague-9lk4y/
eBooks: https://support.pld-literacy.org/en-au/article/the-pld-ebooks-how-can-they-be-used-what-is-the-copyright-policy-ptfya8/
PLD’s Copyright Policy: https://support.pld-literacy.org/en-au/article/copyright-and-terms-of-use-of-pld-literacy-15tkcer/
ISBN :
9 781925 769463
ISBN :
9 781925 769463